The next morning I met Tadeusz Kafarski for a tour of the city. He was with Józef Staszewski, the director of the Żychlin branch of the Association of Children of War. Because Józef was born in 1929, he remembers wartime better than Tadeusz, who was only a year old when the Nazis invaded. The two sometimes disagreed about details, but together they reconstructed for me Jewish life in Żychlin. As they pointed to the buildings that stand here and now, their descriptions transported me back and forth through time, to prewar life, wartime murder, and communist era absence. I had the odd sensation as I did so many times on this trip of being both here (in the present) and then (in the past), my mind trying to reconcile what stood before my eyes with what used to be. My guides led me back in time with varied fragments of information:
On Łukasieńskiego Street, we passed concrete apartment buildings built in the 1970s on the site of the second, larger Jewish ghetto.
Mr. Helmer, the richest Jew in town, lived across from the market square, to the left of Narutowicza Street, in what is now a well maintained two story building.
One block south, near the synagogue (the blue Star of David on the map below) on Kilińskiego Street, we passed the former home of a Jewish doctor, a building that used to be a dairy collection point, and another that was the preschool Tadeusz attended. A man named Merc lived nearer the synagogue. Behind some houses was the Jewish slaughterhouse, but Christian Poles also bought meat from there.
Jews and Poles lived side by side, even though this part of town was predominantly Jewish. Today, this section of town is run down though these particular buildings seem in good shape.
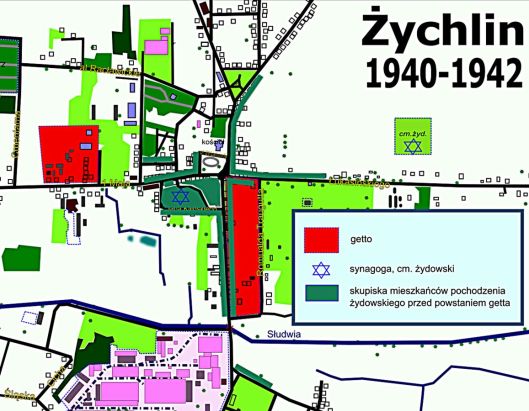
Map of Żychlin 1940-42 showing the ghettos in red, the first one is on the left and the second is on the right. The dark green shows the main areas where Jews lived–note that most were not in what became the ghetto. That meant gentiles had to move out of the ghetto areas when the Jews were forced to move into them.
As we wound through the dusty streets, the contemporary residents stared at us suspiciously, though some who know my guides greeted them, “Dzień dobry (Good day).”
The patch of tall weeds in front of the synagogue (on Jana Kulińskiego Street) used to be a fenced garden. The garden continued to be maintained after the war, even though the Polish residents used the synagogue as a warehouse, as did the Nazis. The lower sections of the windows were bricked in and new doorways were installed in the sides of the building to facilitate loading and unloading.

What’s left of the Żychlin synagogue. Note the windows used to extend much father down, and the more recent doorway (now blocked) added when the building was used as a warehouse. The weedy area in the foreground used to be a fenced garden.

Pan Józef beside the site of the well and mikvah

Worn stones–something I learned to value as a student archeologist. These were used in place of asphalt before World War II
As a child, Józef went inside several times with his parents, though he could only describe the general layout of the interior. The candlelit altar was on the east wall, the main entrance on the west. Above the entrance was a balcony that would have been for the choir in a church but in the synagogue was for women to pray in. In a neighboring building, the rabbi would change. On the other side of the synagogue were a well (with the best water in town) and mikvah. After the war, everyone used that bathhouse.
Józef said, “There is just one faith; Jews believe in God just like we do.” He declared children played together regardless of religion. He described distinctive aspects of the Jewish population. Men wore head covers and beards. They would take their shoes off in the synagogue, but had to keep their head covered. The Jewish “priest” was the only one with side curls. He wore a black hat, black clothes, and a white shirt. Jews stayed home Friday and Saturday; they didn’t work. They held their hands at their waist and rocked as they prayed. They read scrolls. Jews used to bury their dead in a sitting position with money on their eyes. Men carried the unclothed, shrouded body to the cemetery. They returned to God as they began. When they left the cemetery after the burial, mourners dispersed in different directions . He asked why and was told it was so the spirit doesn’t return home with them.
Are these personal memories or stereotypes picked up from other sources?
My guides told me about a man named Rozenberg. They pointed to the yard of his bakery, and then we walked around to what used to be its storefront on Narutowicza Street. Rozenberg lived in a multi-story home on the other side of the street. He married a Christian named Czajka. Jozek said the Rozenbergs’ children Krysia and Rudek were Jewish. He played with the boy. After her husband died, Czajka married her brother-in-law, a judge. They had two more children. After the war, the family was harassed by the police so they sold all their buildings and went to Israel. One child moved to Norway.
The Germans occupied the town on September 15. At first, they didn’t treat anyone harshly, but they did take their property—first the stores and richer buildings owned by Jews, and then jewelry and everything anyone had that was valuable.
The main entrance to the ghetto used to be across from Rozenberg’s bakery. This was the second ghetto, established later for the poorer Jews. The first ghetto, where the richer Jews were sent, was on the grounds of an old factory outside the center of town. As Jews were forced into the ghetto, Poles whose homes were within the ghetto territory had to move to homes on the other side of the street—homes that had been emptied of their Jewish residents.
In July 1942, the second ghetto was liquidated. It took five hours because thousands of people were loaded onto wagons, and then everything was removed from their homes and segregated into piles. Some Poles helped, forced to work under threat of death. My guides disputed claims that Poles plundered Jewish possessions. They insisted the Germans took everything valuable, then piled up all the remaining dirty and broken things and burned them.
We crossed the street to the main square. Right there in front of the church there used to be a row of market stalls run by Jews. The church owned the land, but didn’t have any problem with Jewish venders. We continued behind the church and across another market square to the town library. This solid stone structure was originally built for Hempel, the Nazi mayor of the town remembered for his cruelty.

My guides Tadeusz Kafarski and Józef Staszewski in the town square

The Żychlin town square

Director of the Żychlin Library, Ewa Andrzejewska

Nazi Mayor Hempel’s villa is now the Żychlin Public Library
Tadeusz told me the wartime mayor’s villa was built with tombstones from the Jewish cemetery. Jews were pressed into service carrying the heavy stones. It was backbreaking labor made more difficult by the extreme heat. When one of the workers asked for a drink of water, the Nazi officer shot and killed him. Then, he held up a stick threateningly and asked who else wants a drink. No one dared ask for water after that. Józef told the story a little differently. He said the man who asked for water was dragged to the nearby lake and drowned.
Pani Ewa Andrzejewska, the director of the library, said her aunt who took care of Hempel’s children described him as ruthless, “A typical German.” He furnished his house with things he took from the richer people in the city. He rode a white horse. She also suggested my guides were a little too invested in showing Poles in a positive light to me—emphasizing heroism and victimization and minimizing complicity. She said that on one hand, Jews and Poles lived peacefully together. She was raised to not feel any prejudice. But on the other, many have negative sentiments toward Jews. She even went further to say Poles are genetically indisposed toward Jews. I challenged her on this saying that since sentiments toward Jews have changed over time, it’s a matter of history, not biology. She still didn’t agree, and repeated that Poles have a problem with this.
A dream of mine would be to help preserve and maybe even rebuild the town synagogue. My hosts said the TMHŻ has looked into turning it into their meeting space. Ewa said the ownership of the building is in dispute. So for now it just sits there, slowly crumbling away.
Leaving town the next day, I was once again stopped at the railway crossing as a train sped by. I didn’t mind having one last moment in this town where my great grandmother lived. I felt saddened and rooted by what I had learned, and grateful for the acquaintances who showed me Żychlin as it is now and as it was then.







 Winter 1946 was cold. All around, snow covered homes, roads, and trees. Long icicles hung from the roofs. On a January afternoon, Ariel came on the snowy road to the home of his relatives. Before the war, together with his sisters, he was there a few times. During his last visit in 1939 Ariel’s father, a merchant from Żychlin, knew that soon Germans would attack Poland militarily. Sixteen-year-old Ariel, a short boy, emaciated after the experience of the camp, walked pensively listening to the scrape of his creaking shoes. In his ears rang what his father once told him:
Winter 1946 was cold. All around, snow covered homes, roads, and trees. Long icicles hung from the roofs. On a January afternoon, Ariel came on the snowy road to the home of his relatives. Before the war, together with his sisters, he was there a few times. During his last visit in 1939 Ariel’s father, a merchant from Żychlin, knew that soon Germans would attack Poland militarily. Sixteen-year-old Ariel, a short boy, emaciated after the experience of the camp, walked pensively listening to the scrape of his creaking shoes. In his ears rang what his father once told him:





















 In Warsaw, the conference
In Warsaw, the conference 








