Tags
affect, Aleida Assmann, collective memory, lapidarium in Wronki, Piotr Pojasek, Shadows of Trauma, Society for Psychological Anthropology Meeting
Healing Collective Trauma: Jewish Heritage Work in Poland is the title of the paper I presented at the Society for Psychological Anthropology Meeting in New Orleans on March 12. Here is the abstract I submitted:
The legacy of the Holocaust weighs heavily on Polish communities that were witness to unspeakable events. The paper examines how collective and personal trauma and recovery are intertwined, particularly in relation to Jewish heritage work in Poland. It emphasizes the affective engagement of heritage workers, most of whom are Catholic Poles, working on local projects intended to bring the history and culture of the community’s absent Jews back into the public sphere. Person-centered ethnography helps to reveal how participants talk about the work they do in relation to notions of self and society, and associated personal and social meanings. It further reveals their particular narratives about past and present relationships between Catholics and Jews in Poland, which they often pose as a challenge to the silences of the socialist era and the present-day reemergence of xenophobic nationalism. As members of the post-memory generation—they grew up with stories about former Jewish residents and the destruction of their communities, but they did not actually experience these events themselves—heritage workers are able to work towards reconciliation in ways that older generations could not. They have coming-of-age stories associated with the moment historical events became real to them, and their emotional distress about the past became the force that compelled them to do something about it in the present. Their personal narratives suggest motivation stems from the convergence of attachment to their native place, a sense of responsibility to those who are no longer present, and a desire to realize a more inclusive community that accepts past and present diversity within the Polish polity.
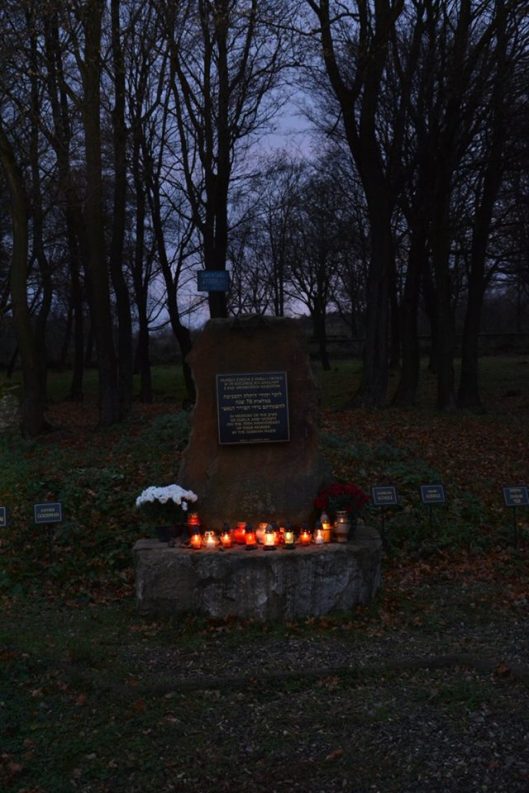
The paper starts with the story of Piotr Pojasek, who grew up in an old farmhouse near Wronki. From childhood, he knew that the curb on his street had been made out of Jewish tombstones during the Nazi occupation, but it was only as an adult that he really realized how wrong that was. And once he became engaged emotionally and morally, he knew he had to do something about it. It took many years, but in 2014, the lapidarium of the tombstones was completed. Applying the categories of memory as defined by Aleida Assmann, I use this case to explore how individual memories can shape social memory, and in turn national and cultural (collective) memory. The point is that individual connections to the past, as Piotr had through the uneasy presence of the tombstones outside his front door and the stories his father told him, are what compelled action. By collecting and sharing historical evidence and the stories of witnesses, social memory about the impact of the Holocaust grew, and developed a resonance for others. Eventually, a large coalition of local, national, and even international sponsors succeeded in building a public monument that revives and perpetuates collective memory of the Jews who lived there, of the inhuman circumstances of their death, and of the Polish citizens who recognize this as an important part of the history of their community.
Commonly, scholarship on collective memory focuses on public symbols and commemorative spaces, and has little to say about the transmission of meaning on the individual level. In my work, I am trying to show the relevance of individual memory workers and their personal engagement with the past as well as their local community. They are the ones who can bring things together, forging personal, affective links that make others care about far distant people and events.



















 Winter 1946 was cold. All around, snow covered homes, roads, and trees. Long icicles hung from the roofs. On a January afternoon, Ariel came on the snowy road to the home of his relatives. Before the war, together with his sisters, he was there a few times. During his last visit in 1939 Ariel’s father, a merchant from Żychlin, knew that soon Germans would attack Poland militarily. Sixteen-year-old Ariel, a short boy, emaciated after the experience of the camp, walked pensively listening to the scrape of his creaking shoes. In his ears rang what his father once told him:
Winter 1946 was cold. All around, snow covered homes, roads, and trees. Long icicles hung from the roofs. On a January afternoon, Ariel came on the snowy road to the home of his relatives. Before the war, together with his sisters, he was there a few times. During his last visit in 1939 Ariel’s father, a merchant from Żychlin, knew that soon Germans would attack Poland militarily. Sixteen-year-old Ariel, a short boy, emaciated after the experience of the camp, walked pensively listening to the scrape of his creaking shoes. In his ears rang what his father once told him:







 In Warsaw, the conference
In Warsaw, the conference 















