This is part II about heritage work in Kutno. The first is Jewish History of Kutno.
While in Kutno, I visited the Society of Friends of Kutno (Towarzystwo Przyjaciół Ziemi Kutnowski). The organization has been active since the early 1970s, and has put out an annual periodical about local history and customs for about 20 years. Most issues of the publication contain an article about Jews. In 2016, these articles were compiled in a book along with other historical materials about Kutno’s Jews, including Holocaust witness reports and photographs, and a list of people who lived in the Kutno ghetto.

Outline of the History of Kutno Area Jews, published by the Friends of Kutno
The chairwoman of the Friends of Kutno Bożena Gajewska is an energetic and upbeat woman. She accepted the position because of her interest in local history and her desire to promote that history among local residents. She isn’t paid for this; she volunteers for the organization after getting off work. The Friends of Kutno have their office in a historic wooden villa that was recently renovated by the city. Most of their funding comes from grants. Over the years, they have placed historical markers where the synagogue, Jewish cemetery, and ghetto used to be. Other recent projects related to Jewish culture include field trips for local residents to the Polin Museum in Warsaw, to a production of a Sholem Asch play at the Yiddish Theatre in Warsaw, and to the Chełmno Extermination Camp, where Kutno Jews were transported when the ghetto was liquidated. Kutno was selected as a site where the Museum on Wheels (a traveling branch of the Polin Museum of the History of Polish Jews) would visit; this happened in August 2016.

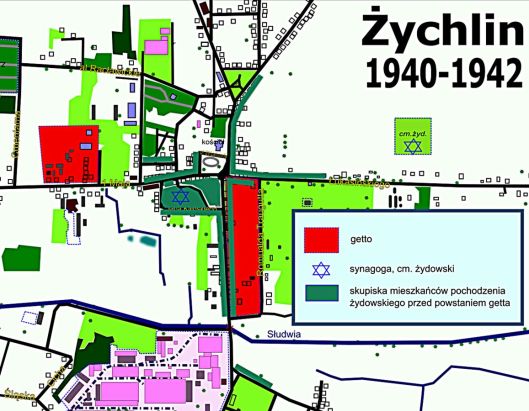
Marker reads, “In this place the 18th century synagogue stood. It was destroyed by the Nazis during World War II, evidence of the hatred of one human to another, and to his works.”
Pani Bożena says she’s noticed that orientations toward Jews have improved since the Polin Museum has opened. Thanks to the Museum, you can talk about Jews, whereas before, the word “Jew” had negative connotations, and was even used as an insult. This made people unsure what to call practitioners of the Jewish faith. Polin has helped to rehabilitate the term. While this may seem like a manifestation of the particularly fraught relationship between Poles and Jews, Mark Oppenheimer just published an opinion piece in the New York Times (Sunday, April 23, 2017, “Reclaiming ‘Jew’”) in which he notes that it’s the same in the US. “Jew” is almost never used as a noun; rather, the adjective “Jewish” is used, as in “Jewish people” or “I’m Jewish” (never “I’m a Jew”). Oppenheimer quotes the comedian Louis C. K. who called “Jew” a funny word “because ‘Jew’ is the only word that is the polite thing to call a group of people and a slur for the same group.”
The Polin Museum has also contributed to a surge of activity related to Jewish history and culture throughout Poland. This has led some townspeople to complain to the Friends of Kutno, “Why is everything always about Jews?” Bożena says she reminds these people that the Friends are interested in all aspects of regional history, and Jews were a part of that history. They address plenty of other topics, as well. For example, they recently published the biography of a native son who was an ultra nationalist during the period when the majority of Kutno residents were Jews (I can’t remember his name but maybe someone reading this can remind me).
Pani Bożena drove me to see some historical sites around town. The Jewish cemetery is on a hill overlooking a neighborhood of concrete apartment buildings. The hillside is covered with tall grass and wildflowers, and crisscrossed by dirt tracks where people walk their dogs, kids play, and people hang out. Many leave their trash behind. The Friends of Kutno recently put up signs around the cemetery that say “Here is the resting place of Kutno Jews, who settled in the city from the beginning of the 16th century. The cemetery located on this hill was established in 1793. Jews were buried here until March 1943. Please maintain its solemnity.” Below this historical information is the reminder, “Keep in mind as you go into this vast expanse that this is a cemetery; people are buried here, you walk on their graves, even though there are no longer tombstones…” Further, the sign states the cemetery is a registered monument and thus legally protected, and any vandalism is subject to a sentence of imprisonment. Nevertheless, within just a few months, four out of six such signs were vandalized. The metal poles were snapped at ground level. Bożena condemned the destruction, but also minimized it as the work of thoughtless hooligans (as opposed to a deliberately antisemitic act). In September, the poles were replaced and the signs stand once again.
We passed people with dogs as we walked to the top of the hill to an older monument. It contains the same historical information as the new metal signs in Polish and Hebrew (but not the reminders about proper behavior and legal issues), and is shaped like two adjoining tombstones. Heading back down the hill, past some children playing, we saw the bases of some grave markers peaking out of the grass. Many tombstones were recovered and are stored at the Kutno Museum.
Bożena dreams of building a fence around the cemetery so there will be a more substantial barrier against further vandalism. They have received all the necessary approvals, but are in need of funding.
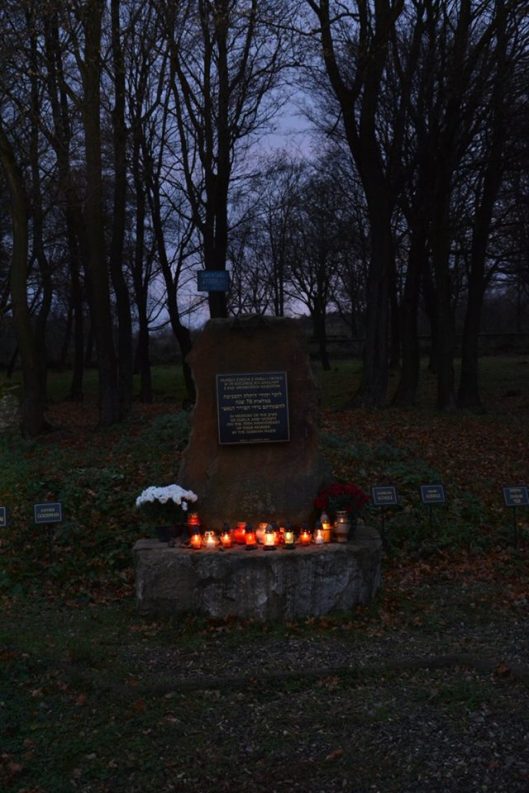
From the cemetery, we went on to the site of the ghetto, which is outside the center of town on the grounds of a former sugar factory. The factory was used by various industries after the war, but now is closed. The buildings, some dating from the late 19th century, stand behind a high fence and a guard patrols the site. Historic markers tell the story of the ghetto. A granite plaque reads:
Here on the terrain of the former Konstancja Sugar Factory
Germans established a ghetto for the Jewish population of Kutno and the surrounding area.
After its liquidation in 1942, the surviving Jews perished in the camp at Chelmno.
Honoring their memory, the People of Kutno.
Kutno, April 1993
A more recent sign contains a bit more historical information in both Polish and English (if you want to read it, click on the photo below to enlarge it).
Bożena told me that over 8000 people lived in the ghetto from 1940-1942. Those who got there first occupied all the most obvious places, so later arrivals had to build shacks from scrap wood, or find ways of populating balconies and any other inhabitable space throughout the large factory hall. In 1942, they were all transported to the camp at Chełmno by train (the tracks are right across the street from the factory) and by truck.
Thinking about the people I met in Kutno (and elsewhere), one thing I am trying to sort out is why Christian Poles get involved in Jewish heritage projects. Not surprisingly, the reasons are varied. One is interested in historical artifacts; he has no political agenda. Another of my companions tried to place this history into a more pro-Polish framework. He explained that the Nazis forced Christian townspeople to do horrible things as part of a strategy to damage relations between Poles and Jews. “All people really want is to live in peace (Chcą w spokoju żyć)”, he continued, “Poland is in the heart of Europe, a pretty terrain that has historically been attacked from all sides.” Others feel personally drawn to Jewish culture. One of my acquaintances in Kutno believes she has Jewish heritage. She seems to understand my quest for my own family history. “It’s important to know where you’re from,” she told me. She hasn’t found anything as concrete as my family photograph (the one I use at the top of the blog) to confirm her feeling that she has Jewish roots. All she can point to are allusions in family stories she remembers from childhood, and sometimes people have told her she looks Jewish. But anyone she could have asked has passed away.
But what’s clear from my visits to Kutno is that fragments of Jewish history remain, and some have been marked as such thanks to the efforts of a small group of residents who think it is important to include the stories of Kutno’s Jews in the history of their town.









































 In Warsaw, the conference
In Warsaw, the conference 



