Tags
Latvia, Lithuania, memorial art, Memory keepers, Riga, Vilnius
I wasn’t looking for Jewish history in Vilnius but it found me. The synagogue, still functioning as a house of prayer for the few thousand remaining Lithuanian Jews, is a half block from my hotel.
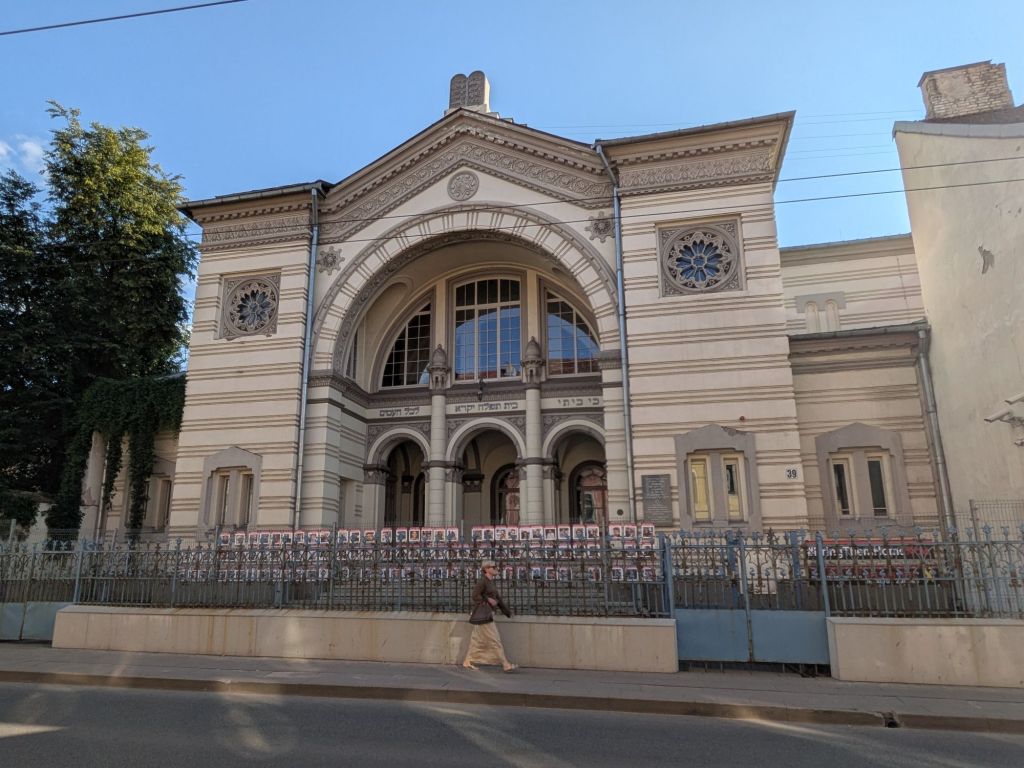

I signed up for a Vilnius with Locals walking tour of Jewish Vilnius, the so-called Jerusalem of Lithuania. We spent 3 hours exploring the Jewish quarter. In some sections, Soviet-era concrete buildings took the place of the prewar structures blown to rubble when the WW II ghetto was dismantled.

Other areas escaped destruction and retain their prewar appearance. As we meandered through narrow cobblestone lanes, Kristina our tour guide explained how much of the city’s Jewish story was silenced during the Soviet occupation, the period from 1940 to 1990 when the country was a republic within the Soviet Union. During that time, nobody talked about the Jews who had made up 45% of the city’s inhabitants before the war.



Kristina explained that this lost history only began to be rediscovered after Lithuania regained independence in 1990. Since then, scholars have been translating and writing about thousands of pages of documents that survived in hiding for 50 years. Many were collected by a group of people called the Paper Brigade who made it their mission to preserve all the documents in the YIVO Archive, a massive repository of Yiddish resources. Much of the archive found safety in New York. Today, the archive is split between Vilnius and New York.
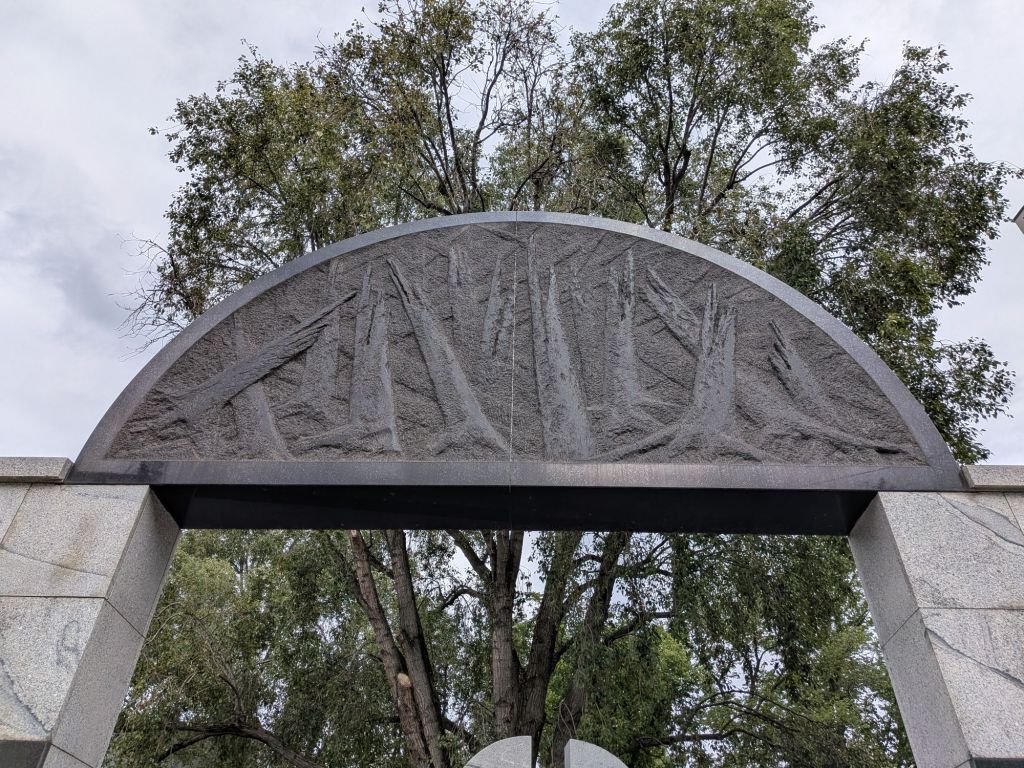
As more has been learned about The Jews of Vilnius, artwork, memorials, and institutions have made the story public. The Walls That Remember project stencils images from archival photos onto the walls of the former Jewish Quarter.
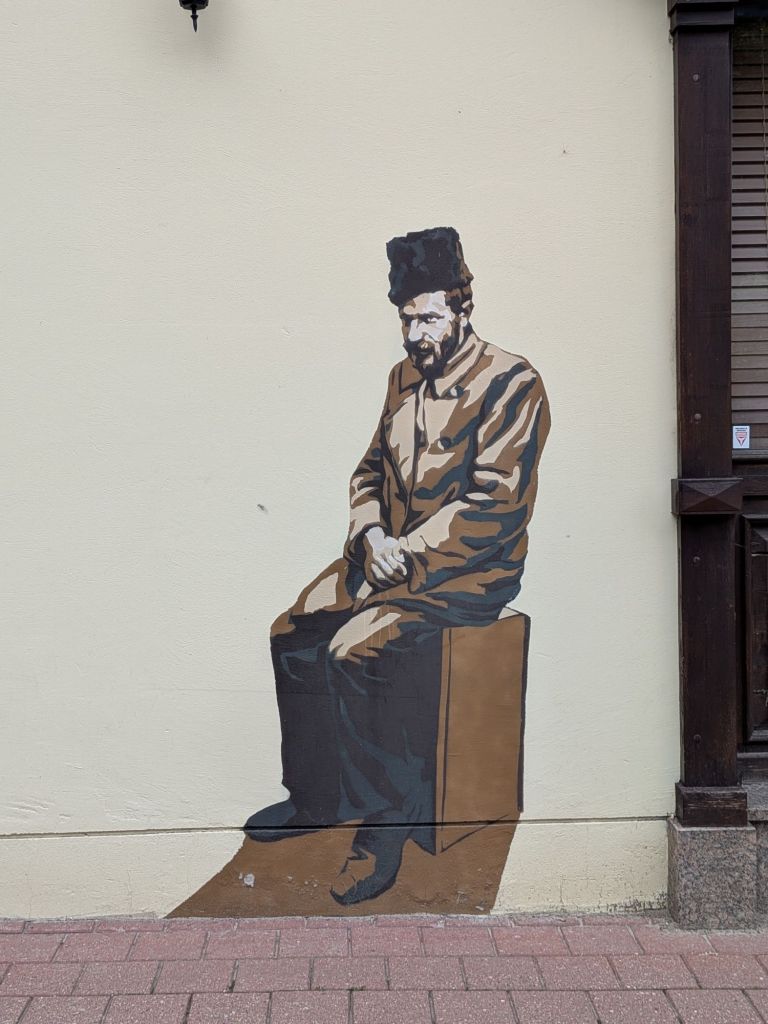



Remembered with a statue are: Zemach Shabad, a doctor known for his kindness who cared for the poor; Rabbi Elijah Ben Solomon (1720 – 1797), also called the Gaon of Vilnius; and singer Leonard Cohen, who had roots in Lithuania.
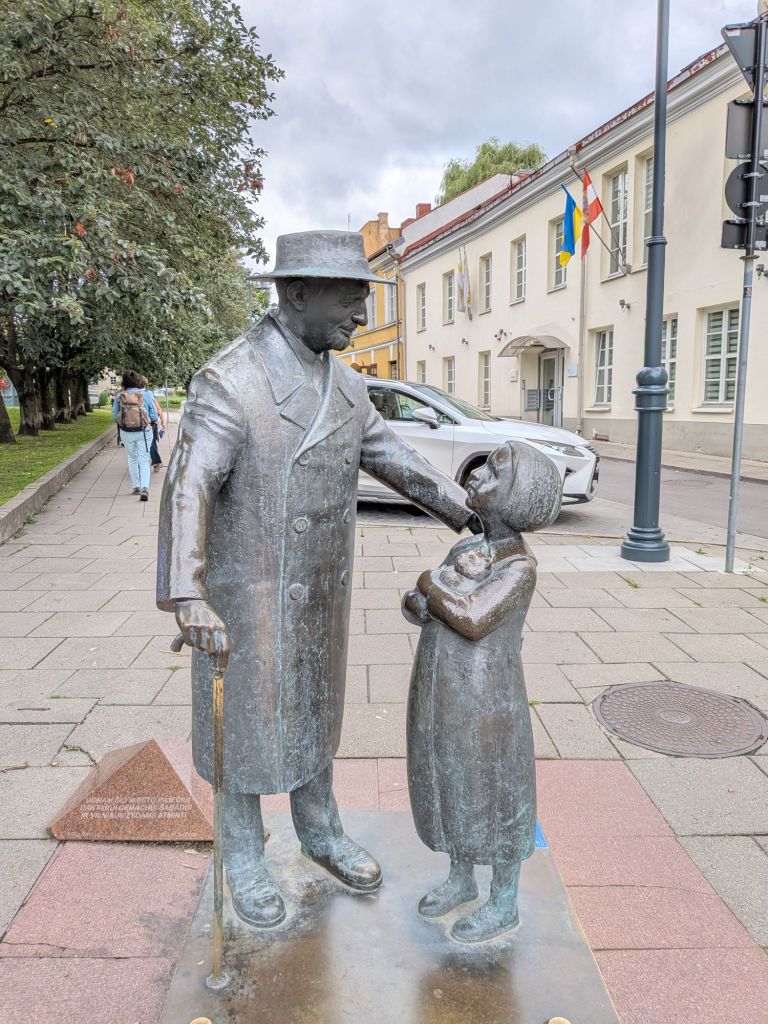


Jews first came to Vilnius as merchants before the 14th century. They were granted privileges by the Lithuanian rulers by the late 14th century. In Vilnius, they settled in the Jewish Quarter; other ethnic groups like Germans each settled in their own quarter of the city. By the time Lithuania was absorbed into the Russian Empire at the end of the 18th century, these ethnic enclaves were less rigid, and Jews could be found throughout the city along with other ethnic and religious inhabitants.
Vilnius was an important center for the growth of Yiddish language and culture, which explains why it was one of the places the Yiddish Scientific Institute (YIVO) was founded in 1925.
After a brief period of national autonomy from 1922 to 1940, Lithuania, like the other Baltic States, became a battleground between Stalinist USSR and Nazi Germany. When Hitler’s forces invaded in 1941, as many as 95% of the Jewish inhabitants were murdered.
Under Communism, the Choral Synagogue continued to operate, though it functioned more as a cultural organization than a religious one (at least officially). Since 1990, the Jewish community remains active at the synagogue. The interior can be viewed for just 2€. Whereas before the war, this was more of a reform synagogue, the current congregation is conservative. Women attend services on the upstairs balcony or behind a curtain on the ground floor.




While on the tour, another participant and I struck up a conversation. Suzanne just completed a two-week tour of Jewish Poland with others of Jewish descent seeking to reconnect with the homeland of their ancestors. It was more than a historical trip, fusing spirituality and rituals within their encounters with Jewish spaces. For instance, at the grave of one participant’s ancestor, they did their own version of feldmestn, a ritual practiced by women; they measured the grave with wax, from which they made a candle.
I bonded with Suzanne over the importance of reconnecting with your Jewish origins, and also because of our shared appreciation for the individuals working in Poland to preserve Jewish memory. She called them memory keepers, a name that perfectly captures the role they play. I will use the term in my future writing about these memory keepers.
In Riga, the capitol of neighboring Latvia, Jewish markers continued to find me. On the building next to my hotel is a memorial marker for someone who saved Jews during the German occupation, and around the corner stands the synagogue. Also, during a walking tour of the city, I met Dimitri and his son Shiloh, reconnecting with their Jewish Latvian roots.