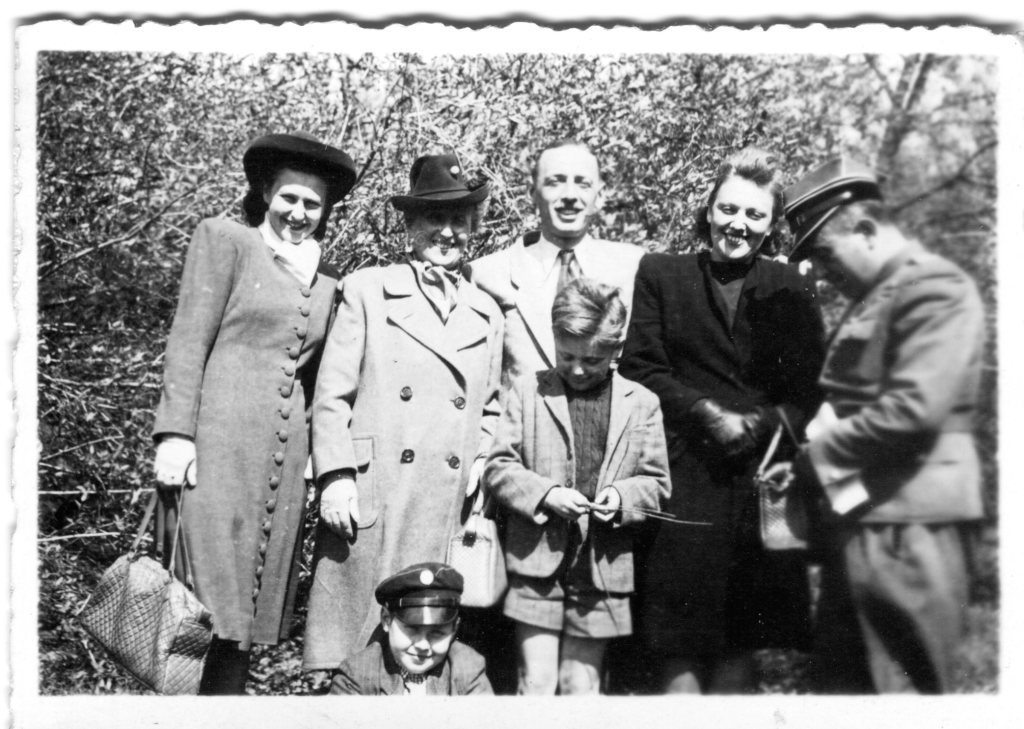
I met my cousin Pini Doron in 2013 when I found his family tree online and wrote to ask if we might be related. He asked for proof, so I sent him the photo in the header of this blog, which he recognized from his own copy. He wrote back “welcome to the family” and ever since I have felt embraced by my extended family in Israel, with Pini at the heart of it. The photo, which includes both of our grandmothers, confirmed that we are cousins.
Last week, we were contacted by Nitay Elboym, who writes for the MyHeritage Hebrew-language blog. He decided to write about our family in commemoration of Holocaust Remembrance Day. It’s a story of connections and separations that span a century.
You can find it in Hebrew at the Internet news service YNet:
and in the MyHeritage blog:
I’ve attached the text in English. I used Google Translate and then edited it. This is the article that appeared in the MyHeritage blog. The YNet version only has minor differences.

Colorized photo of the family from about 1916. Marysia’s grandmother is sitting on the left and Pini’s grandmother is standing on the right
Thanks to a photo and a family tree: a Holocaust survivor son has found family members who disappeared
By Nitay Elboym
April 21, 2020
74-year-old Pini Doron of Hod Hasharon is a longtime MyHeritage user who built a family tree for many years dating back to 1800. Pini thought he had already finished his search, when he received a message with an old family picture. This time, he realized immediately, it was an extraordinary discovery.
“I get a lot of inquiries from people who think they’re related to me,” Pini says. “I am usually skeptical of my relation to them, so I politely ask everyone to explain how we are connected. In this case too, when I received the message, I responded that I would love to know what our family relationship is,” he recalls.
“Actually, at that time, I was pretty much at the beginning of my family history research,” recalls Marysia Galbraith, a professor of anthropology at the University of Alabama, USA. “I was looking for bits of information wherever possible. But when I saw Pini’s family tree on MyHeritage, I knew it was about me, I just didn’t know how. In short, I had no idea how to prove to him how I was related to his family tree, so I just sent the only picture I had. Besides my grandmother, I didn’t know who the people were. Then he answered me ‘Welcome to family.’ His reply almost made me cry. ”
Operation Rescue
The Piwko family lived in the town of Wloclawek, Poland. At the outbreak of World War II, Pini’s grandparents – Pinchas Kolski and his wife Rachel (nee Piwko) – and their two children, Mirka and Samek, were left there while Pini’s father was saved because he and his two brothers were sent to Israel before the war to work the family lands in Kfar Ata. “Because their city of residence was close to Warsaw, they were transferred to the Warsaw ghetto right at the beginning of the war, around 1940,” Pini says. “In the ghetto, Samek was murdered, and my grandfather died of illness. So my grandmother and her daughter Mirka were left alone, looking for a way to survive.”

Mirka and Rachel Kolski at Pinchas Kolski’s grave in the Warsaw Ghetto
Meanwhile, Rachel’s sister, Halina, lived in relative safety outside the Warsaw ghetto, because after divorcing her first Jewish husband, she remarried a Christian man named Zygmunt Bereda. “Rachel and Halina’s father were not ready to hear about this relationship. So, when she married a Christian, he sat shiva on her,” said Pini. “Her sisters tried from time to time to keep in touch, but because of their father, the connection got weaker.” Halina and Rachel’s father, who passed away around 1930, could not have imagined that it was precisely the person who, because of his religious identity, he rejected, would save not only his daughters, but also his other descendants.
When Halina told Zygmunt that her sister was in the ghetto alone with her daughter, he decided to come to their aid despite the risk involved. “Zygmunt was a very successful businessman with a lot of property. In addition, he probably had many connections, which opened doors to him that were closed to others,” explains Marysia. “He used these connections to forge documents for Rachel and her sister, which allowed them to escape the ghetto.”

Halina Bereda, Marysia’s grandmother. She and her Christian husband saved the family

Zygmunt Bereda. A Polish Christian who saved the family of his Jewish wife
But the matter did not end here. Zygmunt and Halina protected the two after they left the ghetto and hid them in buildings they owned throughout the war. At the same time, they were able to forge additional documents that allowed them to leave Poland to Switzerland, and from there, in 1949, the two immigrated to Israel.
“Years of disconnection ended thanks to a surviving photo and family tree on the MyHeritage website. Ever since we started chatting, I have found that Marysia isn’t only a wonderful person, she is also a thoughtful researcher,” says Pini. “She has set up a blog where she writes personally and collects her interesting findings. Everything she does is well organized, backed up by documents, and she knows how to find almost everything. She even studied Polish, which probably helps her a lot in genealogical research.”
The wheel turns over
At the end of the war, Warsaw was devastated by the bombings. The many businesses and houses that Zygmunt owned were also destroyed. He and Halina lost their property and had no place to live. The rescuers now needed help, and the one who came to their aid was the former wife of Samek, Rachel’s son who died in the Holocaust. After the war Halina and her daughter Maria, Marysia’s mother, immigrated to the United States and settled there.
“The truth was kept from us,” says Marysia, who has grown up as a Christian all her life. “For years, family members have been whispering about being Jewish, but never really getting into it. I have spent a long time trying to figure out why my mother and grandmother hid their Jewish heritage and why they were not in contact with Rachel. I think the trauma of the Holocaust left a deep scar on my grandmother. She thought, “If they don’t know, then it won’t hurt them.” That’s probably why they didn’t keep in touch with Rachel and her descendants in Israel.”
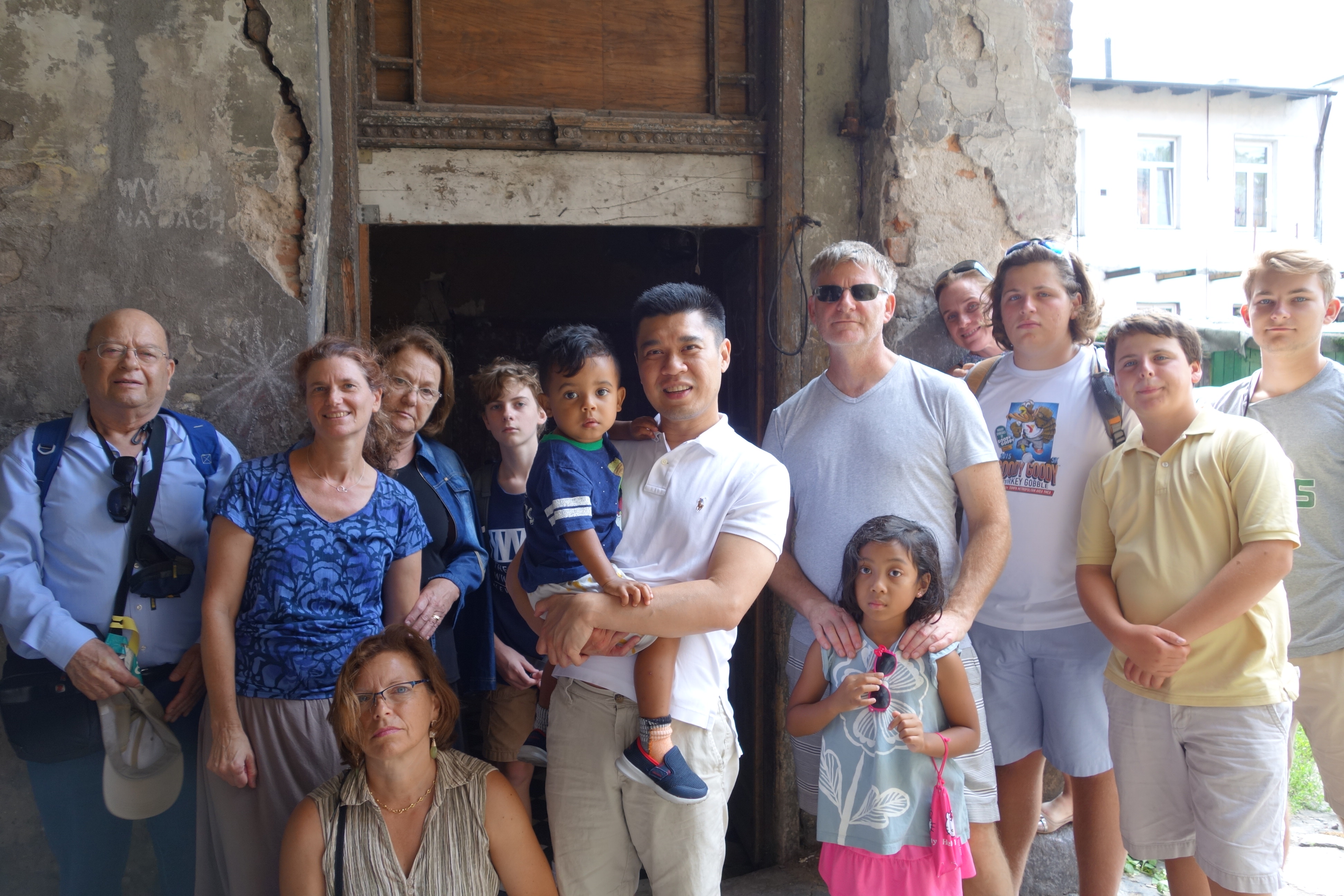
Since the family tree has linked Pini to Marysia the two speak regularly, and they have also met in Israel and in Poland with other family members. “When we went to the graves of our families, the sight was unusual. On one side of the cemetery wall are Jews with a rabbi, and on the other side are Christians with a priest,” Pini recalls. “But what is important? In the end, we are human beings and destiny connected us together.”

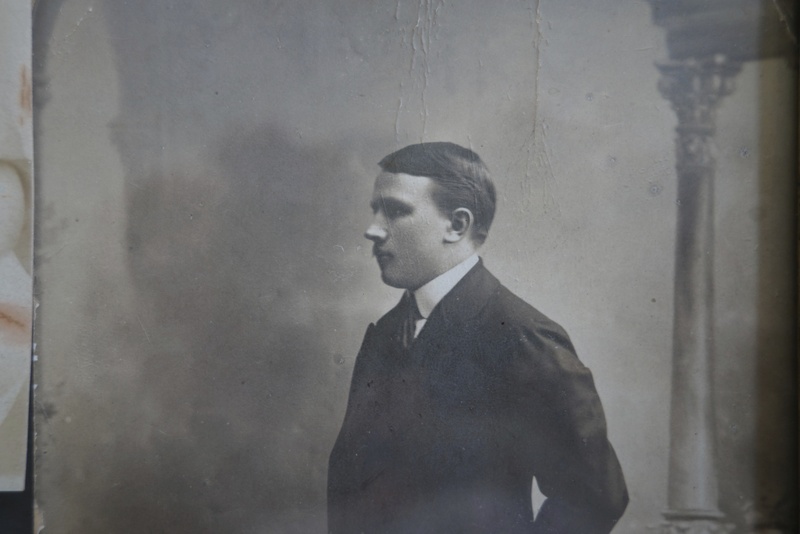
During the roots journey to Poland. Pini stands to the left and beside him Marysia
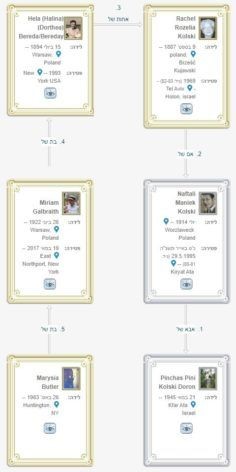
Pini’s Tree showing the family connection between Pini and Marysia
The image that led to the discovery – now in color
To revive the old image that made the exciting discovery, the company’s investigators used the MyHeritage In Color ™ auto-coloring tool and sent the result to Pini and Marysia. “It’s wonderful,” says Marysia. “I’m going to share the colorized picture with my family, including my 90-year-old aunt who will be especially happy.”

Colorized photo of the family from about 1916