I have been calling my project a family memoir since the beginning, well before I read In the Garden of Memory (the English translation was published by Weidenfield and Nicolson in 2004). My family’s story overlaps with author Joanna Olczak-Ronikier’s in other ways, too. The social world of Warsaw was intimate enough that it seems likely our families knew about each other even if they weren’t directly acquainted. Joanna’s relatives, the Horwitzs and the Mortkowiczes, were central figures in the social circles my Babcia also frequented, those occupied by writers, artists, publishers, and professionals. Both families have Jewish origins, and each assimilated, though to varying degrees.

Joanna, her mother Hanna Olczak, and her grandmother Janina Mortkowicz didn’t deny their Jewish origins in the way my mother and grandmother did. Still, they frequented many of the same places around Warsaw. When Janina, then Horwitz, was a child, her “consolation prize” for check-ups at the dentist were a visit to Lourse Café on Krakowskie Przedmieście for chocolate (15). This was in the 1880s, so decades before my grandfather Zygmunt Bereda gained an interest in the business. During the 1930s, Joanna’s cousins attended the same high schools as my mother and uncle. Girls attended the Klementyna Hoffmanowa High School, while boys went to the Stefan Batory High School.
The book also gives me some insight into marriage customs during my Babcia’s generation. “According to Jewish tradition, finding suitable husbands for one’s daughters was a basic parental duty,” Olczak-Ronikier writes. “Marriage was too serious a matter to be contracted for love. After all, it concerned two people’s future, and that of their offspring. The older generation took charge of bringing the couples together, involving family, friends and a professional matchmaker” (32). Things were changing rapidly in the late 19th century, though, and just like I have observed among Babcia’s siblings, older children were more bound by tradition while younger children were more inclined to choose their own pathway. In Olczak-Ronikier’s family, the younger children were drawn to socialism and communism.
By the next generation, Joanna’s mother Hanna was the first and only family member to marry a non-Jeweven and to change her religion. Olczak-Ronikier says, it “did not provoke any particular reaction among her relatives” (184). She was not excluded from the family because of it, unlike my grandmother Halina, whose father sat shiva and treated her as dead after her marriage to a Catholic. Olczak-Ronikier’s family was far more secular than Babcia’s, though. Perhaps in part this is because the Piwkos lived in provincial cities where the pull of religious tradition was stronger. My grandmother was drawn to Warsaw for the opportunities it offered for her to remake her life.
Another parallel I see between our family stories is in the internalized antisemitism Joanna experienced. As a child in the 1930s, she didn’t want to be Jewish, especially when she became the object of the anti-Jewish taunts of other children. She explains, “Among Jews who had decided to assimilate, a huge role was played by ambitions relating to the level of Polonization they had achieved. When the parents, through their looks, language and religious customs, were a reminder of the environment that the children had made such an effort to get out of, family love and loyalty were severely put to the test. Nowadays it is hard to imagine how painful this process of tearing oneself away from one’s roots must have been” (71).
Maks Horwitz, her great uncle, put it this way: “They were ashamed of their origin. Understandably, they never denied it among those who knew about it. But even here, in deed, word and gesture they tried to prove and convince others that they felt themselves to be completely and utterly Polish and that they were entirely rid of their Jewishness” (111).
Members of both families survived the war by adopting Aryan identities. Babcia was able to live more in the open than Olczak-Ronikier’s family because she had been distanced from her Jewish origins since the 1920s, and also because her Catholic husband was well enough positioned to bribe the Nazi authorities to look the other way. As in my family, the women of Joanna’s family took a few years off their age on their false documents (92). During the Warsaw Uprising, when the area they lived in was overrun by the Germans, Olczak-Ronikier’s family escaped via the underground sewers, as did my mother. With the destruction of the capital, both families took the same path out of the city, traveling with a crowd of refugees south to Krakow, where they remained until the end of the German occupation. (268)
Joanna’s cousin Ryś Bychowski was born the same year as my mother. He attended Stefan Batory High School, just like my Uncle George who was just a couple of years older. It seems likely they knew each other, and its possible they could have been friends. Their lives might have overlapped during the war, as well. Ryś escaped to safety in the US with his parents in 1941, only to volunteer for the Polish Airforce, which operated out of Britain. My uncle was a paratrooper, while Ryś became a navigator. Ryś joined as a Polish patriot, unwilling to remain in safety when his people were subject to Nazi oppression. For him, the fact that he was Jewish only added to his resolve. He wanted to liberate Poland and the Jewish people. While in Britain, he confronted the horror of the mass annihilation of the Jews, made even more unbearable when his friends and comrades exhibited indifference, or in some instances satisfaction, that the Jews were killed. Olczak-Ronikier explains, “His Polish-Jewish identity had always seemed something quite natural to him, yet in view of this and similar episodes he came to the conclusion that he had to make a choice” (295). He decided he could never live in Poland again, even though he remained committed to the fight against Nazism.
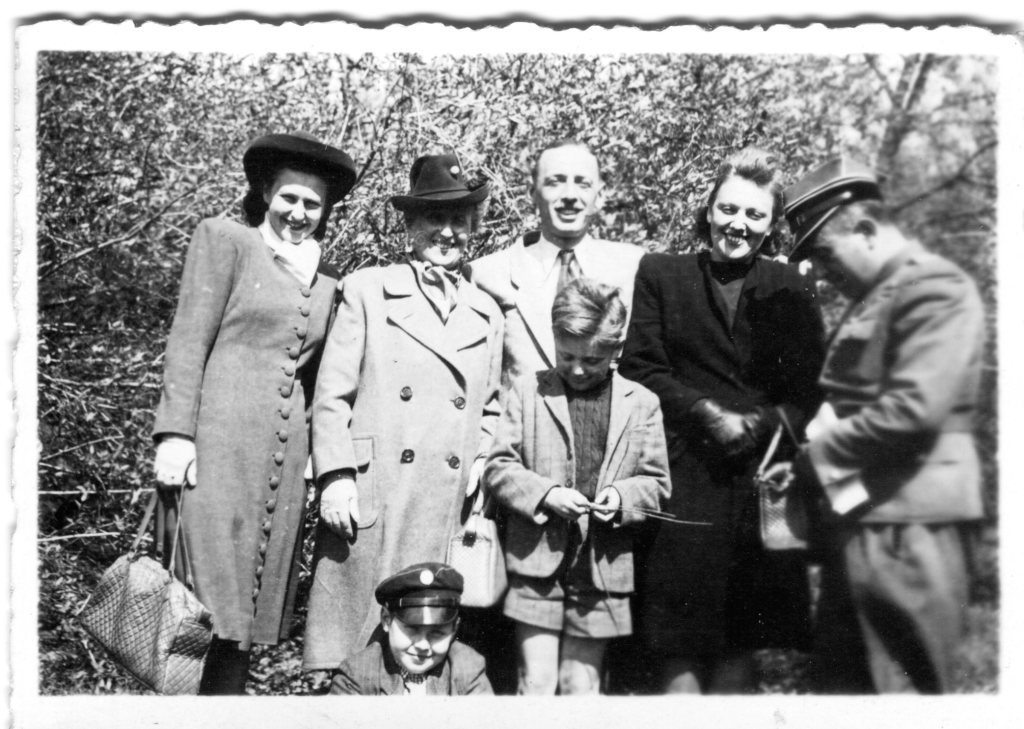

The evolution of Ryszard’s view of Poles helps me understand the deep anger and resentment so many Jews feel toward Poland. It’s something I have recognized before, and wondered why they direct their fury more strongly toward Poles than to Germans. In a letter to his father in 1943, Ryś Bychowski explained in clear and emotionally resonant terms; “I do not want to be a second-class citizen ever again […] Above all I’m afraid of knowing the whole truth about the reaction of Polish society to the extermination of the Jews. I cannot live with or talk to, I am not able to work with people who found it possible to ignore their destruction, occupy their homes and denounce or blackmail the survivors” (296). This was an intimate betrayal, not by a sworn enemy but by comrades and neighbors. It was exclusion from the group he felt himself to be a part of. No wonder it cut so deeply.